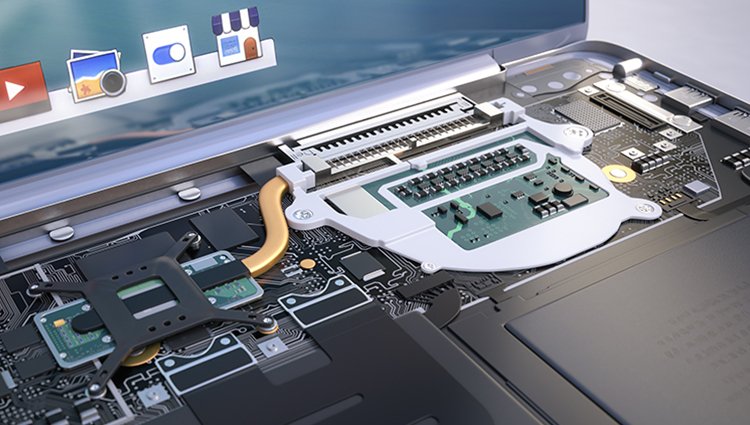
Introduction to Ventiva and Ionic Cooling Technology
Ventiva is an innovative tech startup that is making significant strides in the field of thermal management through its pioneering ionic cooling engine (ICE) technology. Established with the aim of redefining cooling systems, Ventiva addresses the growing challenges faced by modern electronic devices in dissipating heat efficiently. The company’s flagship product, the ICE, introduces a groundbreaking approach to cooling that eliminates the need for traditional moving parts typically found in mechanical fans.
The ionic cooling engine operates based on the principles of ionic wind, a concept rooted in electrohydrodynamics. By applying a high electric field to the air, the ICE generates a flow of ions that propel air away from the device, thereby facilitating effective cooling without the mechanical components that can contribute to wear and tear over time. This method not only extends the lifespan of electronic equipment but also enhances energy efficiency, which is crucial in a world increasingly reliant on sustainable technologies.
The transition from conventional mechanical fans to advanced solutions like ICE represents a significant leap forward in the technological landscape. Mechanical fans, while effective, often come with drawbacks such as noise generation, vibration, and limited heat dissipation capabilities under varying operational conditions. As electronics continue to evolve with higher performance demands and compact designs, the need for innovative cooling solutions becomes increasingly evident. Ventiva’s ionic cooling engine not only responds to these demands but also places the company at the forefront of a competitive market where efficiency, reliability, and sustainability are paramount. In this context, the ICE technology is not just a notable advancement; it is a potential game-changer in addressing the cooling challenges inherent within modern electronic applications.
How Ionic Cooling Engine Technology Works
The Ionic Cooling Engine (ICE) technology represents a transformative approach to thermal management by leveraging the principles of ionization. This innovative system functions through the generation of charged particles, or ions, which interact with the surrounding environment to create airflow without the use of traditional mechanical fan blades. The initial step in this process involves the ionization of air molecules, a phenomenon that occurs when an electrical charge is applied, resulting in their fragmentation into ions and electrons.
Once generated, these ions are propelled across heat-emitting surfaces within the cooling system. Through this movement, they effectively absorb heat from these components, leading to a reduction in temperature. The design of the Ionic Cooling Engine allows these charged particles to flow continuously, creating a steady stream of ionized air that circulates around the heat-generating elements. By harnessing the natural behavior of ions, ICE technology eliminates the mechanical complexities and limitations associated with traditional cooling systems.
Crucially, this method utilizes the principle of repulsion and attraction between charged particles to facilitate airflow. Positively charged ions are attracted towards negatively charged surfaces, enabling a dynamic movement that promotes extensive air circulation. This process not only enhances the efficiency of heat dissipation but also minimizes the noise and vibration typically associated with conventional fans. Importantly, the lack of moving parts in the Ionic Cooling Engine leads to reduced wear and tear, extending the lifespan of the device.
Overall, the mechanics of ICE technology provide a sophisticated alternative to standard cooling solutions. By emphasizing the movement of ionized air and harnessing the unique properties of charged particles, this technology showcases its potential to revolutionize how we approach cooling in various applications, delivering effective and efficient thermal management.
Applications and Benefits of ICE Technology
The Ionic Cooling Engine (ICE) technology developed by Ventiva represents a significant advancement in thermal management systems, particularly within consumer electronics such as laptops and wireless chargers. By employing this innovative cooling approach, manufacturers can improve product performance while enhancing the overall user experience.
One of the primary applications of ICE technology is in laptops. Traditional cooling systems often rely on fans, which can contribute to noise and increase the device’s overall bulk. In contrast, ICE technology operates silently, as it eliminates the need for moving parts. This not only creates a more pleasant working environment but also extends the laptop’s lifespan by reducing mechanical wear and tear. The compact design of ICE allows for thinner, lighter laptops without sacrificing cooling performance, appealing to users who prioritize portability and aesthetics.
Moreover, ICE technology can also be effectively integrated into wireless chargers. With the increasing demand for efficient charging solutions, effective heat management is imperative. The quiet operation of ICE significantly contributes to a better user experience, allowing devices to charge without disruptive noise. Additionally, the energy efficiency of ICE minimizes power loss, rendering wireless charging solutions more viable for everyday use while contributing to longer-lasting batteries across devices.
The implications of adopting ICE technology extend beyond mere aesthetics and user comfort. The removal of moving parts inherently leads to enhanced reliability and lower maintenance needs. As consumers become more conscious of device performance, energy efficiency, and silent operation, ICE technology positions itself as a leading solution. Ultimately, the incorporation of ICE into laptops and wireless chargers highlights the potential for a quieter, more efficient future in consumer electronics, with significant repercussions for both manufacturers and users alike.
Challenges and Future of Ionic Cooling Engine Technology
The Ionic Cooling Engine (ICE) technology, despite its innovative design and potential advantages, faces multiple challenges that could hinder its widespread adoption in various applications. One significant concern is the cooling efficiency compared to traditional cooling methods, such as fans. While ICE provides silent operation and reduced size, its effectiveness in maintaining optimal temperatures in high-performance systems, such as gaming laptops and powerful servers, remains to be fully demonstrated. The performance metrics of cooling efficiency must be rigorously tested against established cooling solutions, which might affect user acceptance and market penetration.
Moreover, the cost of manufacturing ICE technology presents another major obstacle. Advanced manufacturing techniques and materials required for Ionic Cooling Engines may lead to higher production costs. These costs could result in elevated prices for end consumers, limiting accessibility, primarily in sectors sensitive to budget constraints. Manufacturers will need to find ways to reduce production costs without compromising quality and performance, which is vital for competitive viability in the cooling technology market.
Additionally, scalability remains a daunting challenge, particularly for larger systems, such as data centers. The development of effective ICE solutions that can handle the significant thermal loads generated by extensive server arrays is crucial. As the demand for efficient cooling solutions in large-scale applications increases, it is essential for engineers and researchers to innovate in scaling ICE technology without losing efficiency or increasing costs disproportionately.
Looking ahead, future developments in ionic cooling technologies may offer solutions to these challenges. Research may focus on optimizing the design and materials of ICE systems to enhance overall performance and production efficiency. There could also be opportunities for collaboration across the tech industry, leading to innovations that allow for greater integration of ionic cooling in existing systems. Bearing in mind the obstacles present today, the drive to overcome these issues will likely dictate the feasibility and impact of Ionic Cooling Engine technology across diverse sectors in the coming years.
PC: Ventiva